The AstraZeneca/Oxford University vaccine has been a frontrunner in the race to find a coronavirus jab and has been shown to be 70.4 per cent effective and possibly up to 90 per cent.
How does the AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine work?
The vaccine – called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 – uses a harmless, weakened version of a common virus which causes a cold in chimpanzees.
Researchers have already used this technology to produce vaccines against a number of pathogens including flu, Zika and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (Mers).
The virus is genetically modified so that it is impossible for it to grow in humans.
The ongoing global clinical trials of the covid-19 vaccine led by @UniofOxford and @AstraZeneca have launched in the US to assess safety, efficacy and immunogenicity of the vaccine for the prevention of covid-19:https://t.co/lyLhK8MfUw
Advertisement— University of Oxford (@UniofOxford) September 3, 2020
Scientists have transferred the genetic instructions for coronavirus’s specific “spike protein” – which it needs to invade cells – to the vaccine.
When the vaccine enters cells inside the body, it uses this genetic code to produce the surface spike protein of the coronavirus.
This induces an immune response, priming the immune system to attack coronavirus if it infects the body.
Does it differ from Pfizer and Moderna’s vaccine?
Yes. The jabs from Pfizer and Moderna are messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines.
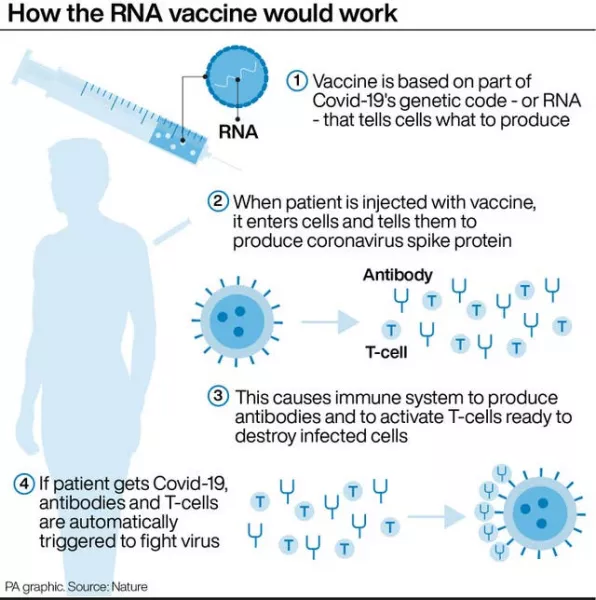
Conventional vaccines are produced using weakened forms of the virus, but mRNAs use only the virus’s genetic code.
An mRNA vaccine is injected into the body where it enters cells and tells them to create antigens.
These antigens are recognised by the immune system and prepare it to fight coronavirus.
No actual virus is needed to create an mRNA vaccine. This means the rate at which the vaccine can be produced is accelerated.
What about antibodies and T-cells?
The Pfizer, AstraZeneca and Moderna vaccines have been shown to provoke both an antibody and T-cell response.
Antibodies are proteins that bind to the body’s foreign invaders and tell the immune system it needs to take action.
T-cells are a type of white blood cell which hunt down infected cells in the body and destroy them.
Nearly all effective vaccines induce both an antibody and a T-cell response.
A study on the AstraZeneca vaccine found that levels of T-cells peaked 14 days after vaccination, while antibody levels peaked after 28 days.
Can the Oxford vaccine be manufactured to scale?
Yes. The British government has secured 100 million doses of the Oxford University and AstraZeneca vaccine as part of its contract, enough for most of the population.
Ireland is part of the European Commission’s vaccines order, which spreads the risk faced by individual EU states by linking countries to multiple vaccines, not just one and by offering purchasing clout.
Deals are signed with Oxford-AstraZeneca, Sanofi-GSK and Janssen, while “finalised contract negotiations” are under way with Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna to provide 460 million doses next year. Ireland will get 4.6 million doses.
Experts hope the Oxford-AstraZeneca jab could be ready to go and rolled out shortly.
Can this vaccine help the elderly?
There have been concerns that a Covid-19 vaccine will not work as well on elderly people, much like the annual flu jab.
However, data from the Oxford University and AstraZeneca vaccine trial suggests that there has been “similar” immune responses among younger and older adults, with Moderna reporting the same.
In a statement earlier this year, Oxford University said its data marked a “key milestone”, with the vaccine inducing strong immune responses in all adult groups.